
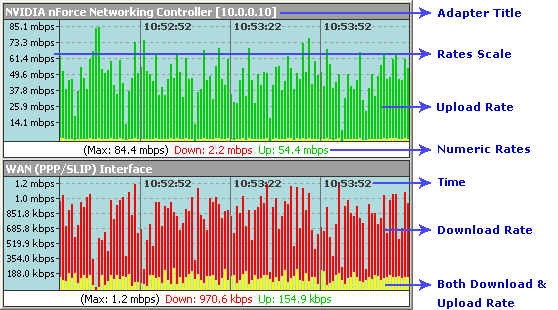
Bandwidth capacity means the maximum data rate a link can transfer. Firms are still using DSL and cable connections to run their business, but service providers have been able to allocate more resources to support these lower-tier Telco options.īandwidth capacity is also an important consideration. Now, those who have the funds can install Gigabit speed to their infrastructure to support the growth in data consumption. It used to be normal for businesses to use low bandwidth services like 56.k modems to transmit information. Upload speed is the speed at which data is sent to its destination, while download speed refers to the rate at which data is received. What people don’t know, however, is that there are actually two different types of bandwidth speed: upload and download. Since most organizations rely on the internet to conduct business-critical operations, internet speed can make all the difference in their success. Thirty years ago, data was sent through physical mediums like the postal service now there are myriad ways to transmit and receive massive amounts of data with the push of a button. Bandwidth is quantified as the amount of data transferred in time, typically measured in bits per second. What I hope to highlight in this article are the different ways to effectively manage bandwidth to maintain peak network performance with a network bandwidth monitor. I would go as far as saying that monitoring your network bandwidth usage is the most critical function for any network administrator. Regardless of what traffic you are monitoring, though, it’s important to understand the bandwidth that is being utilized so you can ensure users are getting the best possible performance out of your network. For example, you can monitor bandwidth speed or capacity you can observe network traffic between devices or general web application traffic. While it used to be that monitoring your bandwidth meant solely focusing on internet traffic, bandwidth monitoring now encompasses a broader range of components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
